Smart polymers: Chains that know when to make the clean cut
Keywords:
Smart polymers, controlled drug release, stimulus-responsiveAbstract
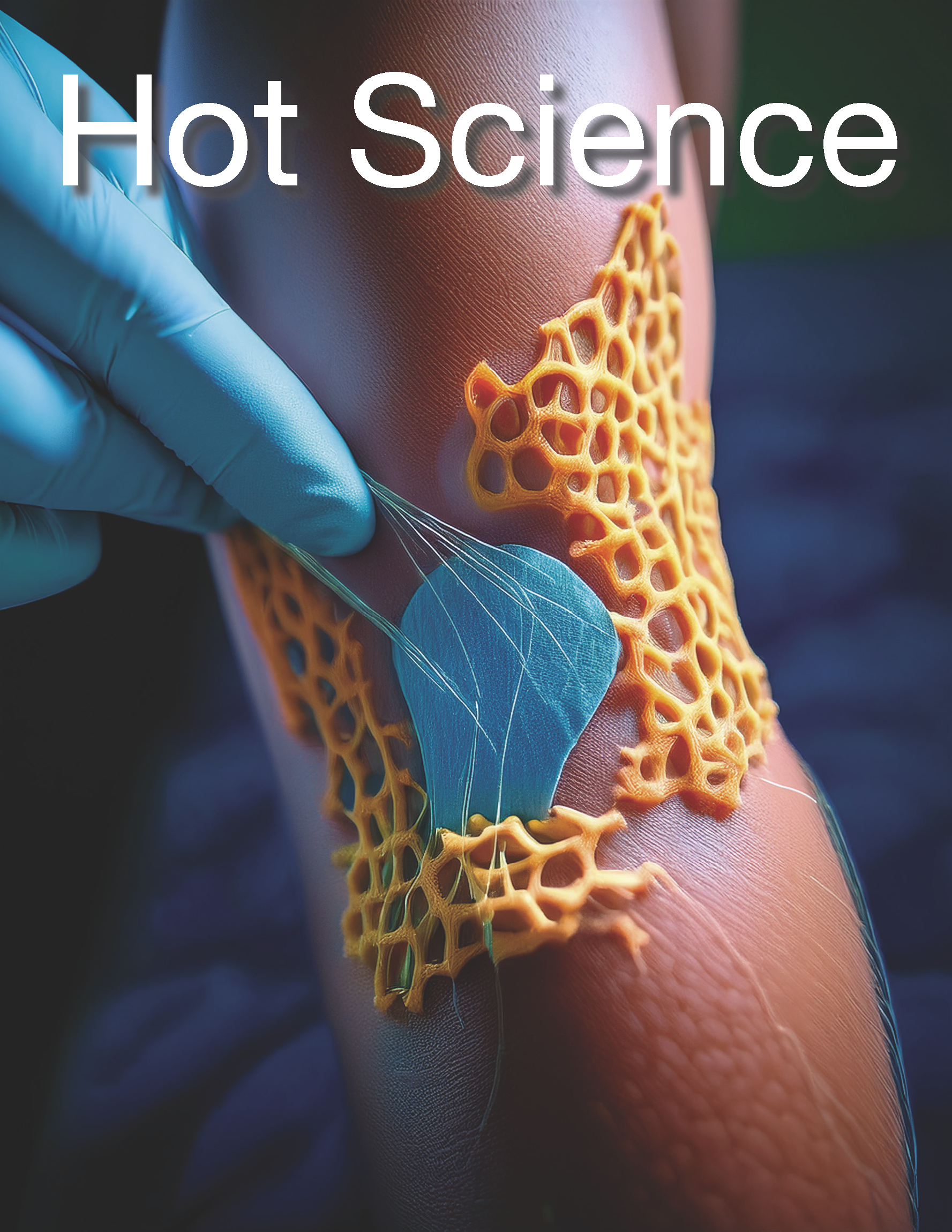
Smart polymers are materials that respond to stimuli, such as temperature or pH, and alter their structure to release drugs in a controlled manner. They function as “molecular guardians” that act only at the precise moment and location, enhancing effectiveness and reducing side effects. At the National Polytechnic Institute (IPN), these principles have been applied to develop an intelligent dressing for chronic wounds, which releases antimicrobial and healing compounds upon detecting an infection. Its low cost facilitates large-scale production and access in vulnerable communities. This approach holds promise for future applications in oncology, regenerative medicine, and infection control.
References
Villanueva-Flores, F., Miranda-Hernández, M., Flores-Flores, J. O., Porras-Sanjuanico, A., Hu, H., Pérez-Martínez, L., Ramírez, O. T., & Palomares, L. A. (2019). Poly(vinyl alcohol co-vinyl acetate) as a novel scaffold for mammalian cell culture and controlled drug release. Journal of Materials Science, 54(10), 7867–7882. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-019-03402-1
Villanueva-Flores, F., & Palomares, L. A. (2022). Low-cost poly(vinyl formal) for heavy metal removal from water of a polluted river. Journal of Water Reuse and Desalination, 12(1), 52–65. https://doi.org/10.2166/wrd.2022.077
Heskins, M., & Guillet, J. E. (1968). Solution Properties of Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide). Journal of Macromolecular Science: Part A - Chemistry, 2(8), 1441–1455. https://doi.org/10.1080/10601326808051910
Convatec. (2024). AquacelTM. https://www.convatec.com/es-co/productos/cuidado-avanzado-de-heridas/marcas-comerciales/pc-wound-aquacel/
Villalobos, C. (31 de mayo de 2024). Parche inteligente para tratar heridas crónicas. Gaceta Politécnica, Instituto Politécnico Nacional (IPN), 174, 13–15.
Balcerak-Woźniak, A., Dzwonkowska-Zarzycka, M., & Kabatc-Borcz, J. (2024). A Comprehensive Review of Stimuli-Responsive Smart Polymer Materials—Recent Advances and Future Perspectives. Materials, 17(17), 4255. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17174255
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Revista de divulgación científica iBIO

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Self-archiving or deposit of the works in their post-publication version (editorial version) is permitted in any personal, institutional or thematic repository, social or scientific networks. The above applies from the moment of publication of the article in question on the website of the Revista de divulgación científica iBIO.




